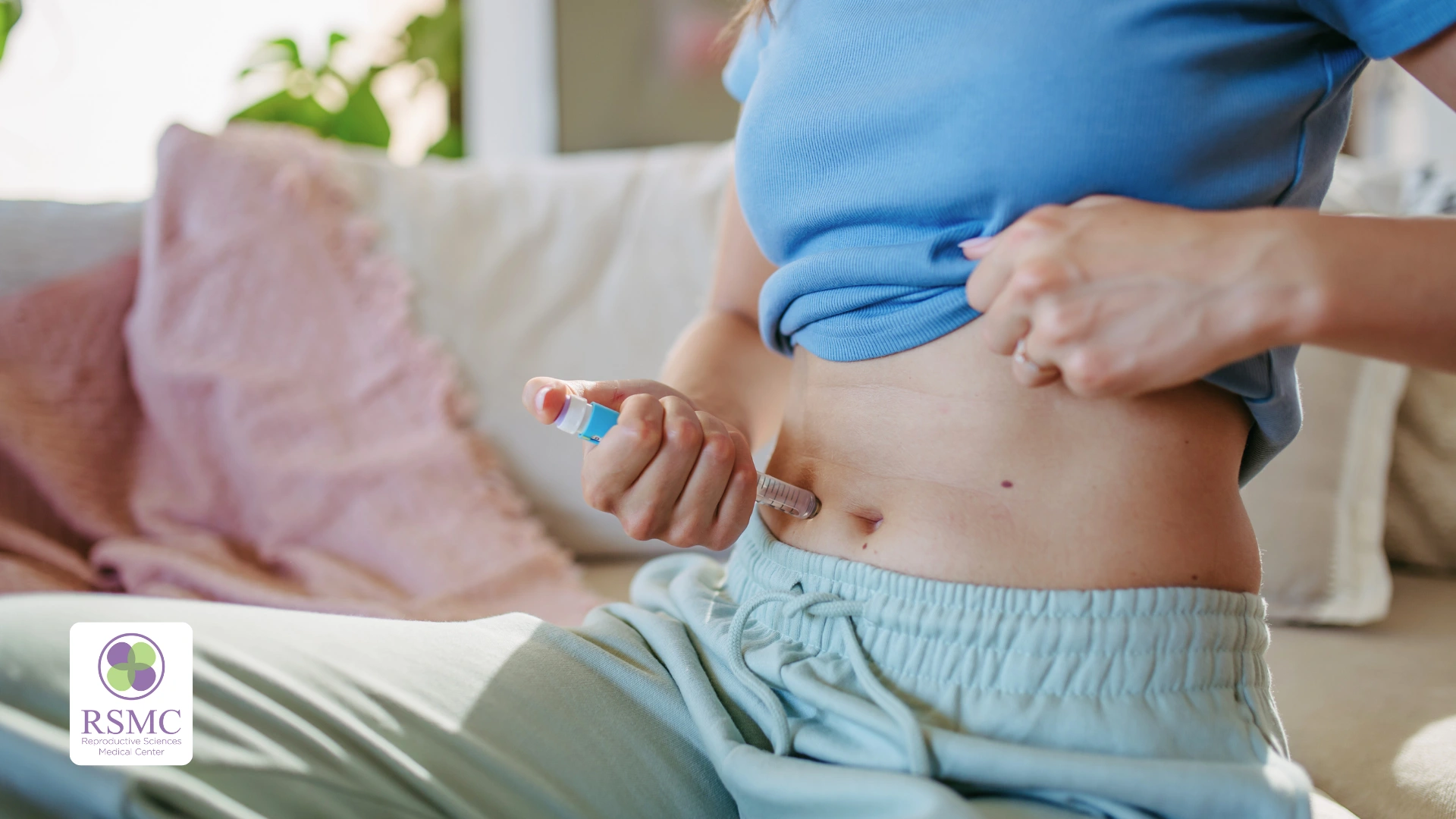
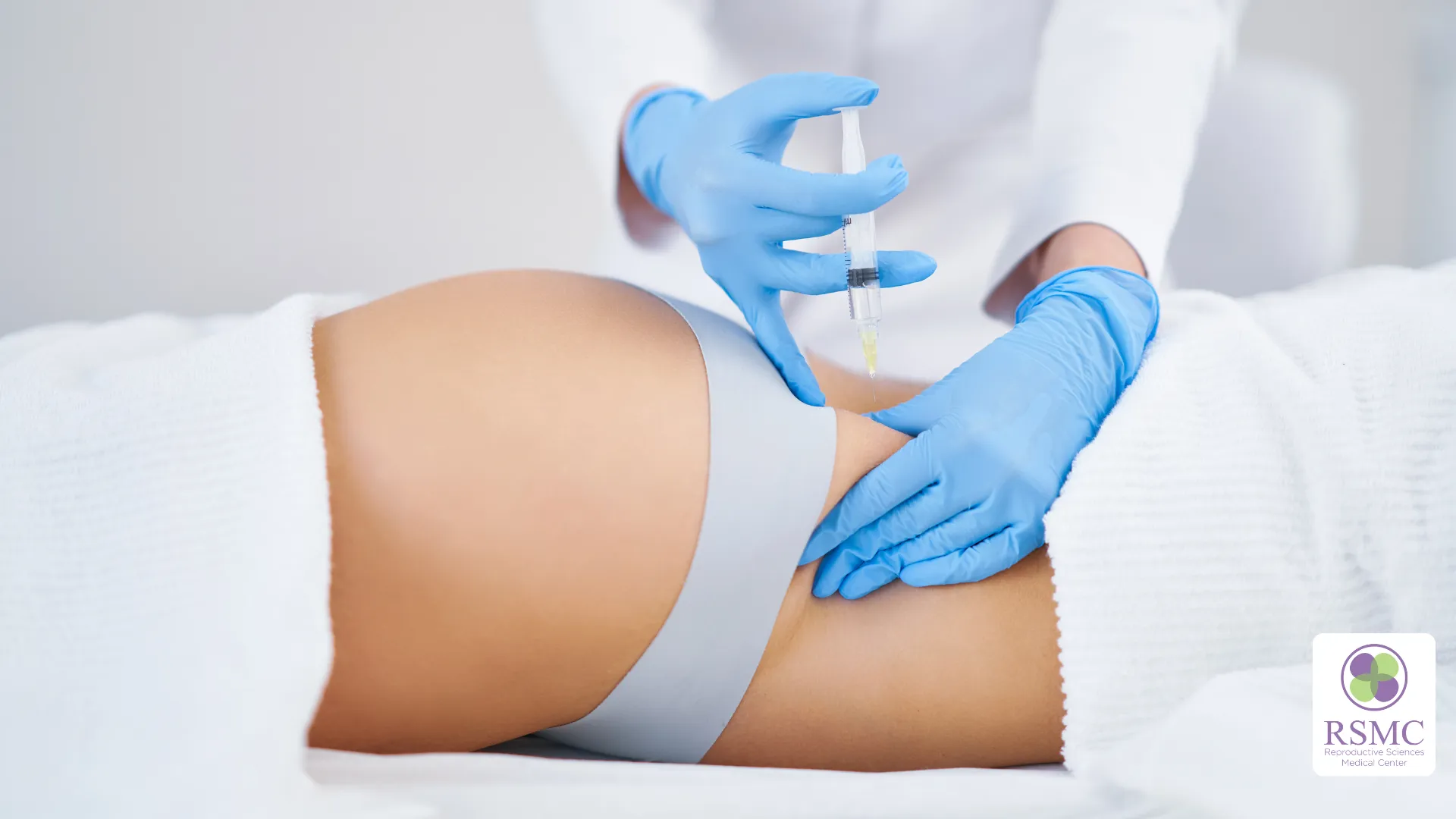
The trigger shot for IVF is essential in improving egg quality and ensuring a successful fertilization process. This injection is an important step in the IVF cycle, as it triggers the final maturation of eggs. Proper administration and timing of the trigger shot are essential to optimize egg development and increase the chances of a successful pregnancy. Understanding how it works, the available options and potential risks can help individuals undergoing IVF achieve better outcomes.
Why the Trigger Shot Is Important for IVF Success
The trigger shot in IVF helps eggs reach full maturity before retrieval. It stimulates meiosis, reducing the egg’s chromosome count from 46 to 23, ensuring the embryo has the correct genetic makeup for healthy development. In a natural cycle, ovulation is triggered by luteinizing hormone (LH), but during IVF, the trigger shot mimics this process to control egg release more precisely.
Administering the trigger shot at the right time is vital. Fertility specialists choose between different trigger shot options, such as human chorionic gonadotropin hCG or GnRH agonists, depending on factors like ovarian response and the risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS).
The trigger shot is important in improving the IVF success rate by ensuring eggs are mature and ready for fertilization, making it an essential part of the treatment process.
Trigger Shot Timing and Its Impact on IVF Outcomes
Administering the trigger shot at the right time ensures proper egg maturation and optimizes the chances of a successful IVF treatment. The timing must align with the development of the ovarian follicles to ensure the eggs are mature enough for fertilization but not overdeveloped.
- Optimal follicle size: The trigger shot is typically given when most ovarian follicles are 18 to 22 mm in diameter. Follicles within this range are more likely to contain mature eggs that can be successfully fertilized.
- Risks of mistiming: If the trigger shot is administered too early when follicles are smaller than 15 mm, the eggs may be immature and not viable for fertilization. Conversely, if given too late, follicles larger than 22 mm may contain over-mature eggs, negatively impacting embryo quality and implantation success.
- Individualized approach: Every patient responds differently to ovarian stimulation, so fertility specialists carefully monitor follicular growth through ultrasound scans and blood tests to determine the precise timing for the trigger shot. This personalized approach helps improve the chances of retrieving high-quality eggs.
Proper timing of the trigger shot is one of the most critical aspects of the IVF process. It ensures that the eggs are ready for retrieval and fertilization, ultimately contributing to a higher success rate and improved embryo quality.
Ovarian Stimulation Cycle: How It Works
The ovarian stimulation cycle encourages the ovaries to produce multiple eggs to increase the chances of successful fertilization. During this stage, hormonal medications are used to stimulate the ovaries, and the trigger shot is administered at the right time to finalize egg maturation before retrieval.
- Hormonal stimulation: Fertility medications, such as gonadotropins, are prescribed to promote the growth of multiple ovarian follicles. Throughout this phase, the patient undergoes regular ultrasounds and blood tests to monitor follicle size and hormone levels, ensuring optimal development.
- Trigger shot administration: Approximately 36 hours before egg retrieval, the trigger shot is administered to initiate the final stage of egg maturation. This ensures the eggs complete meiosis, reducing their chromosome count from 46 to 23 chromosomes and preparing them for fertilization.
Confirming Egg Maturity
After administering the trigger shot, eggs are examined under a microscope to confirm maturity. A mature egg should display a polar body, indicating it has undergone meiosis. However, the presence of a polar body does not guarantee the correct number of 23 chromosomes in the egg. If the chromosome count is incorrect, it can result in an aneuploid embryo, which may lead to failed implantation or miscarriage.
Choosing the Right Trigger Shot: Urinary vs. Recombinant hCG
Selecting the appropriate trigger shot is an important decision in the IVF process, as it directly impacts egg maturation and the overall success of the cycle. The most commonly used options are urinary-derived hCG (hCGu) and recombinant hCG (hCGr). Each type has distinct characteristics influencing its effectiveness, cost, and suitability for individual patients.
Urinary-derived hCG (hCGu)
Sourced from the urine of pregnant women, hCGu has been used for decades in fertility treatments and is known for its reliability in triggering ovulation. It is typically administered in a dose of 10,000 units, effectively stimulating final egg maturation in most patients.
hCGu is generally more affordable than recombinant hCG, making it a preferred choice for cost-conscious patients. However, due to its natural derivation, hCGu may contain some impurities and have slightly varied potency across different batches.
Recombinant hCG (hCGr)
Lab-developed and produced through genetic engineering, hCGr offers high purity and consistency. It is usually administered in a standard dose of 250 mcg, though studies suggest that this dosage may only be 50-70% as effective as the traditional 10,000 units of hCGu.
Many specialists recommend doubling the dose to 500 mcg to achieve comparable results, especially for patients with more follicles. Recombinant hCG is more expensive than urinary-derived hCG but offers precise dosing and a reduced risk of allergic reactions.
Considerations When Choosing Between hCGu and hCGr
- Patient response: Some individuals may respond better to one type than another based on their hormone levels and ovarian reserve.
- Risk of OHSS: Recombinant hCG is sometimes preferred in patients at risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), as it may offer better control over stimulation.
- Cost factors: While hCGu is more budget-friendly, hCGr provides a consistent and reliable option for those who prefer lab-manufactured medications.
Choosing the right trigger shot requires careful evaluation of the patient’s ovarian response, medical history, and treatment goals. Fertility specialists tailor the dosage and type of hCG to ensure optimal egg maturation while reducing potential risks and improving the chances of a successful IVF cycle.
Using GnRH Agonists (Lupron) as a Trigger Shot
GnRH agonists like Lupron are often used as an alternative to hCG trigger shots in IVF. Instead of directly stimulating the ovaries, Lupron triggers the pituitary gland to release a surge of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which naturally promotes egg maturation.
Benefits of Lupron:
- Lower risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), as it leaves the body faster than hCG.
- More natural ovulation induction by mimicking the body’s LH surge.
- Reduced complications for high-risk patients, such as those with a high follicle count.
Challenges of Lupron:
- The LH surge can be unpredictable, especially in women with ovarian suppression treatments.
- It may not be effective for those with low ovarian reserve or pituitary issues.
- Unlike hCG, Lupron requires additional luteal phase support to maintain pregnancy.
Lupron is typically recommended for patients at risk of OHSS or those requiring a gentler stimulation approach. Fertility specialists may also combine Lupron with a low dose of hCG for better results.
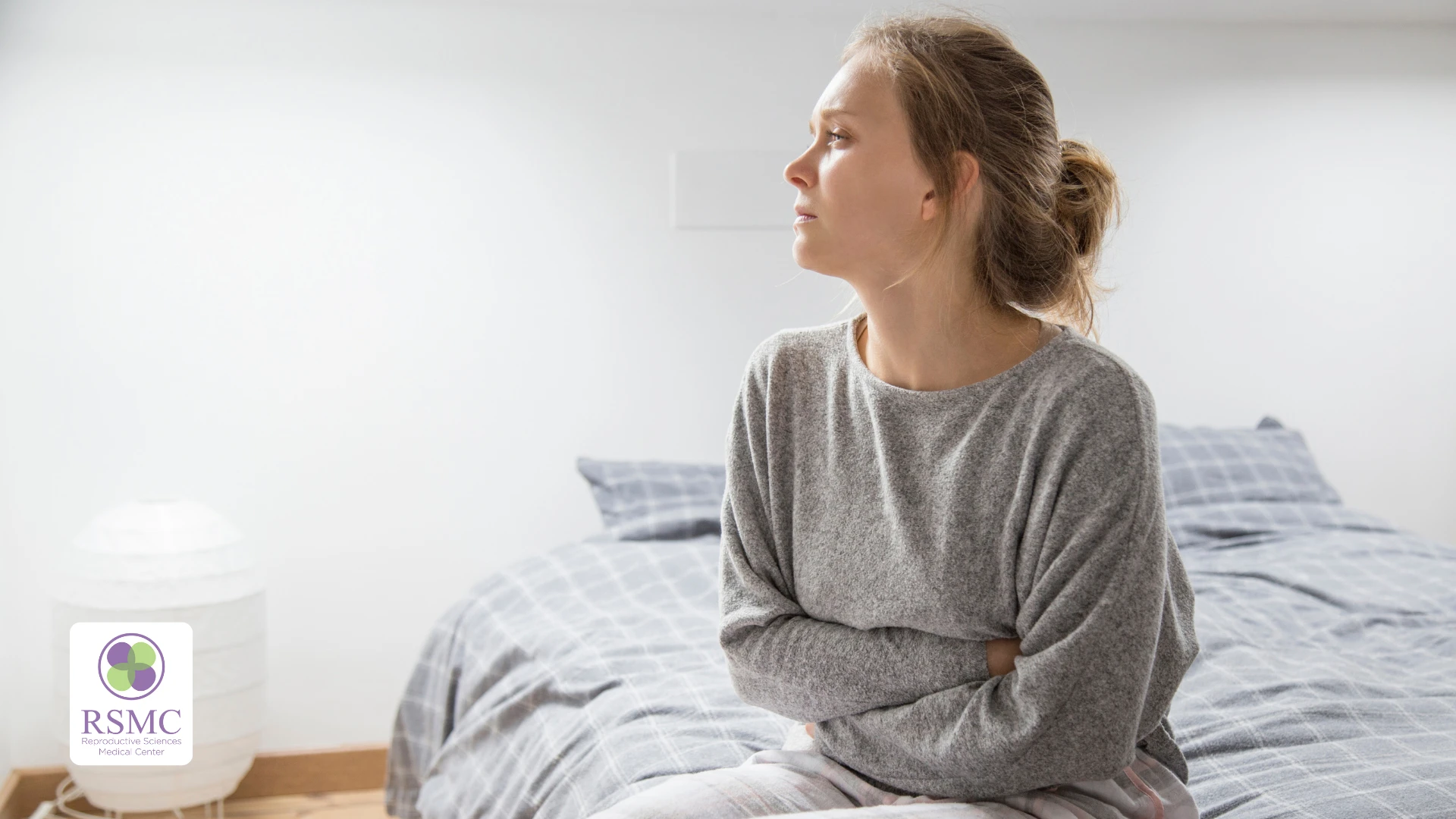
Potential Side Effects of the Trigger Shot
The trigger shot used in IVF may cause a range of side effects, from mild to more severe reactions. Common side effects include:
- Bloating and abdominal discomfort
- Tenderness or pain at the injection site
- Mild nausea and headaches
- Gastrointestinal issues, such as diarrhea or constipation
- Mood swings and fatigue
In rare cases, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) can occur, leading to more serious symptoms such as:
- Rapid weight gain (over 2 pounds per day)
- Severe abdominal bloating and pain
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Decreased urine output
- Blood clotting issues
If severe symptoms arise, seeking immediate medical attention is crucial to prevent complications and ensure a safe IVF process.
The trigger shot is very important in the IVF process, ensuring eggs reach full maturity for successful fertilization. Its proper administration and timing impact the overall success of the treatment, helping to optimize embryo quality and implantation rates. With various trigger shot options available, including hCG and GnRH agonists, fertility specialists tailor the approach to each patient’s unique needs. Understanding the importance of the trigger shot, its timing, and potential risks empowers individuals undergoing IVF to make decisions and improve their chances of achieving a healthy pregnancy.
Table of Contents
- Why the Trigger Shot Is Important for IVF Success
- Trigger Shot Timing and Its Impact on IVF Outcomes
- Ovarian Stimulation Cycle: How It Works
- Confirming Egg Maturity
- Choosing the Right Trigger Shot: Urinary vs. Recombinant hCG
- Using GnRH Agonists (Lupron) as a Trigger Shot
- Potential Side Effects of the Trigger Shot