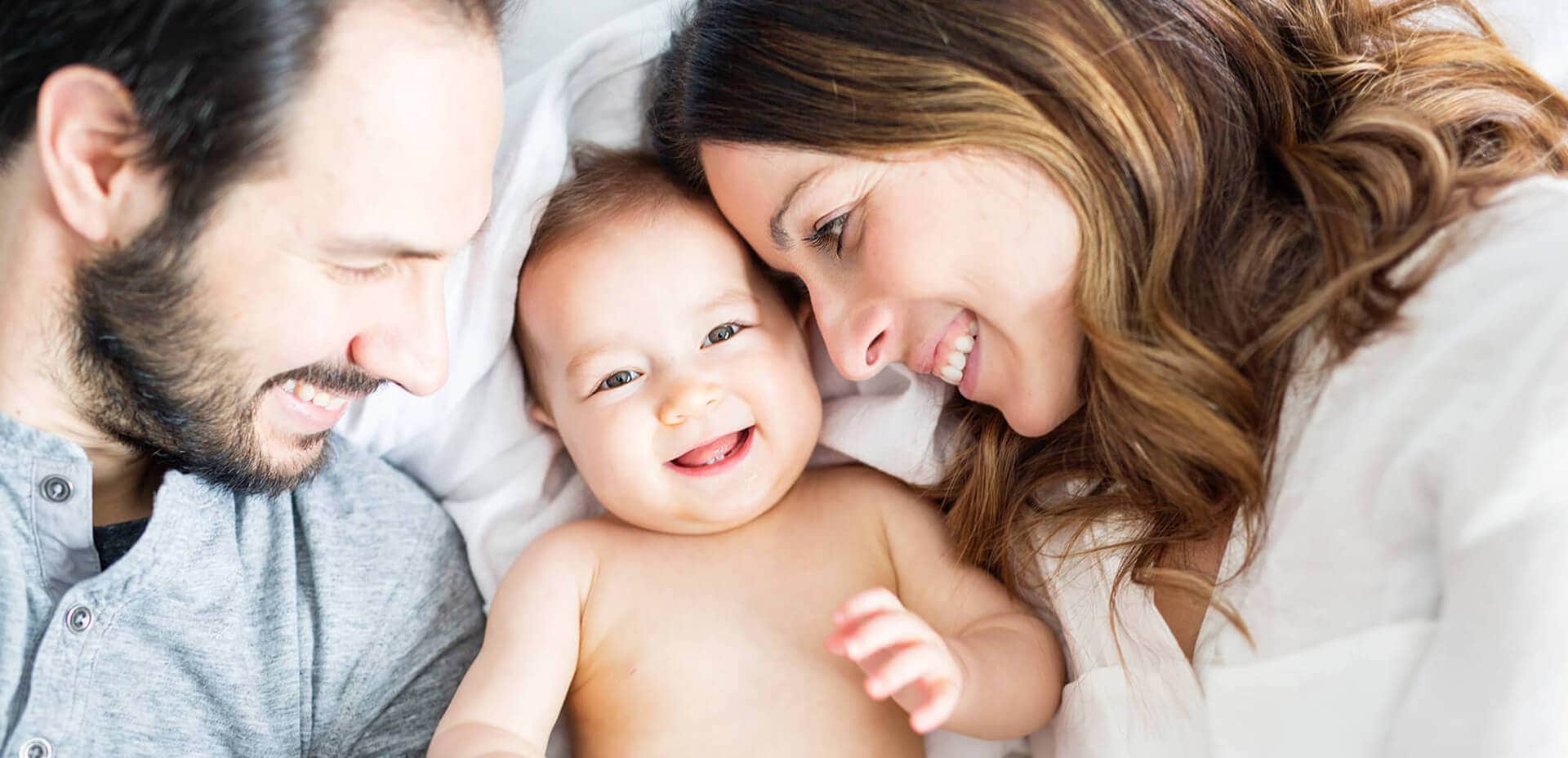
What is the FET Success Rate?

Healthy embryos resulting from an IVF cycle that not transferred to the patient at the end of the cycle can be cryopreserved, or frozen, and stored. When the patient is ready to have another child, her embryo(s) are thawed and transferred to her uterus under physician care.
This process is called a frozen embryo transfer (FET). Some women may freeze all good quality embryos produced in a fresh IVF cycle for FET at a later time. Women may choose this option for fertility preservation or because their hormonal profile and/or uterine lining is not optimal during a fresh IVF cycle.
A patient preparing for an FET has blood testing and ultrasound scans that enable her physician to identify the appropriate point in the patient’s cycle to transfer the embryo(s). Some FET patients may also take hormone medication to prepare for the transfer.
The FET success rate is nearly the same as fresh IVF cycles and have the same primary indicator for success – the maternal age at the time of embryo freezing. Many patients wait several years between the initially freeze of their embryos and attempting a subsequent FET cycle. Any patient, no matter the amount of time between embryo freezing and thawing, can expect nearly the same potential for success as they experienced with the original fresh IVF cycle, because frozen embryos are suspended in time and do not age.